 ZOMİT 2,5 mq/dose nasal spray
ZOMİT 2,5 mq/dose nasal spray
ZOMIT
International non-patented name: Zolmitriptan
Composition
The active substance: 1 ml (dose) of nasal spray contains 2.5 mg of zolmitriptan.
Excipients: benzalkonium chloride, anhydrous citric acid, sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, dexpanthenol, purified water.
Description
light yellow liquid.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Medicine used for migraine. Selective serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists.
ATC : N02CC03.
Pharmacological features
Pharmacodynamics
It is a selective agonist of 5HT1-receptors, an anti-migraine drug.
It has high affinity for 5HT1B/1D receptors and moderate affinity for 5HT1A receptors. Zolmitriptan does not show significant pharmacological activity against 5HT2-, 5HT3-, 5HT4-receptors, α1-, α2-, β1-adrenoreceptors, histamine H1-, H2-receptors, muscarinic receptors, dopamine receptors of type 1 and 2. Blood vessels and vessels of the dura mater are innervated by afferent fibers of the trigeminal nerve. In animal experiments, zolmitriptan causes vasoconstriction due to its agonist properties with 5НТ1B/1D-receptors of vessels; this condition is associated with inhibition of calcitonin gene, vasoactive intestinal peptide and substance P peptide release. When a migraine attack occurs, vasoconstriction and inhibition of the release of neuropeptides lead to an improvement in the condition, in particular, a decrease in pain intensity and migraine-related nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and phonophobia no later than 1 hour after taking the drug. In addition to its peripheral effect, zolmitriptan affects the nuclei of the brain stem, which are involved in the mechanism of development of migraine attacks, which explains the persistent effect of repeated use during the treatment of several migraine attacks in one patient. As the main effector neurotransmitter during a migraine attack, vasodilation is noted due to the activation of reflex arousal supported by orthodromic fibers of the trigeminal nerve and parasympathetic innervation of the cerebral vessels through the release of vasoactive intestinal peptide. Zolmitriptan blocks this reflex arousal and release of vasoactive intestinal peptide
Pharmacokinetics
Absorb
After oral administration, zolmitriptan is rapidly and well absorbed (at least 64%).
75% Cmax is achieved within 1 hour; the determined concentration in the blood plasma is maintained for the next 4-6 hours. Absorption of zolmitriptan is independent of food intake.
When taking a single dose, the AUC and Cmax of zolmitriptan and its active metabolite in the dose range from 2.5 to 50 mg are proportionally dependent on the dose.
Average absolute bioavailability is about 40%.
Accumulation of the drug was not observed after repeated use.
Distribution
Its binding to blood plasma proteins is low (about 25%).
Metabolism
It undergoes metabolism in the liver, and 3 main metabolites are formed: indole-acetic acid (the main metabolite in blood plasma and urine), N-oxide and N-desmethyl analogues. The N-desmethylated metabolite (183C91) is active, while the other two metabolites are inactive. Compared to zolmitriptan, N-desmethyl-metabolite (183C91) has 2-6 times higher agonistic activity of 5HT1D-receptors (based on data from animal experiments). The concentration of N-desmethyl-metabolite (183C91) in blood plasma is about half of the concentration of zolmitriptan, and therefore it can be assumed that this metabolite supports the therapeutic effect of Zomit.
Exclusion
More than 60% of the drug taken in the form of a single oral dose is excreted in the urine (mainly in the form of an indole-acetate metabolite) and about 30% in the feces, mostly unchanged.
The mean T½ of zolmitriptan is 4.7 hours. The T½ of its metabolites are approximately the same, suggesting that they are eliminated as they are formed.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
Despite a slight increase in the AUC of zolmitriptan and its active metabolite (16% and 35%, respectively), and a prolongation of T½ by 1 hour (to 3-3.5 hours), compared to healthy volunteers, suffering from moderate to severe renal impairment Renal clearance of zolmitriptan and its metabolites decreases 7-8 times in smoking patients.
When assessing the pharmacokinetics of zolmitriptan in patients with liver diseases of varying degrees of severity, compared to healthy volunteers, an increase in AUC of 94% and Cmax of 50% in moderate hepatic impairment and 226% and 47% increase in severe hepatic impairment, respectively, were shown. During liver diseases, the formation of metabolites (including the active metabolite) decreases. AUC and Cmax values for metabolite 183C91 in the group of patients with moderate hepatic impairment decreased by 33% and 44%, and in patients with severe hepatic impairment, these indicators decreased by 82% and 90%.
T½ of zolmitriptan was 7.3 hours in the group of patients with moderate hepatic impairment, and 12 hours in patients with severe hepatic impairment. T½ of metabolites was 5.7 hours, 7.5 hours and 7.8 hours.
Pharmacokinetic interaction of the drug with ergotamine was not noted.
The pharmacokinetics of zolmitriptan in healthy elderly subjects are similar to those in healthy young subjects.
Compared to the use of free zolmitriptan alone, the concomitant use of zolmitriptan with ergotamine/caffeine was well tolerated by patients and did not lead to an increase in the frequency of adverse reactions or changes in arterial pressure (BP).
Selegiline (MAO type B inhibitor) and fluoxetine (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) do not affect the pharmacokinetic parameters of zolmitriptan.
Indication of use
- Elimination of migraine attacks observed with aura.
- Elimination of migraine attacks without aura.
- During migraine aura without headache (silent migraine).
Contraindications
- Uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- ischemic heart disease (IHD);
- angiospastic angina (Prinsmetal’s angina);
- cerebral circulation disorders or transient ischemic attacks in the anamnesis;
- peripheral vascular diseases;
- combined use of ergotamine or its derivatives or other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors;
- associated with other additional impulse conduction pathways, VPU syndrome or arrhythmias;
- creatine clearance below 15 ml/min;
- hypersensitivity to any component contained in the drug.
Special instructions and precautions
Elderly patients should be prescribed the drug with caution (the safety and effectiveness of using Zomit in patients over 65 years of age has not been studied).
The drug Zomit has a strong effect on migraine associated with menstruation, with or without aura. The gender and age of the patient, the duration of the seizure, the presence of nausea before the use of the drug and the use of common drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks do not affect the effectiveness of the drug.
The drug can be used only during a confirmed diagnosis. Before using the drug, it is necessary to exclude other possible serious neurological conditions.
There is currently no information on the use of Zomit in hemiplegic or basilar migraine. Migraine sufferers may be at increased risk of developing cerebrovascular disease. Hemorrhagic stroke, subarachnoid stroke, ischemic stroke and other disorders of cerebral circulation have been reported in patients taking serotonin 5Н1B/1D-receptor agonists.
When using drugs of this class (serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptor agonists), spasms of coronary vessels, angina or myocardial infarction have been noted very rarely. It is recommended to examine the condition of the cardiovascular system before starting treatment with the drug for patients with a high risk of developing CKD. In very rare cases, serious cardiovascular complications may develop in patients without a history of cardiovascular disease.
During the use of the drug Zomit (like other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors), there are reports of atypical sensations in the heart area. If chest pains or symptoms of CKD appear, the use of Zomit should be stopped until an appropriate medical examination is carried out.
The drug Zomit (like other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors) can cause a slight transient increase in AT, regardless of the presence of arterial hypertension in the anamnesis; very rarely, such elevation of AT is clinically significant. Rarely, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions have been reported when using Zomit (like other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors). Overuse of antimigraine medications can lead to increased headache frequency, potentially necessitating discontinuation of treatment.
Zomit drug should not be used for the prevention of migraine attacks.
Use when liver functions are impaired
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
In case of severe liver function disorder, the recommended maximum dose of the drug taken within 24 hours is 5 mg.
Use when kidney function is impaired
For patients with impaired renal function, Zomit dosage regimen correction is not required.
Use in pediatrics
The safety and effectiveness of the use of Zomit in children and adolescents under 18 years of age have not been established
Interaction with other medicine
There is no information confirming the effects of drugs used together for the prevention of migraine (β-adrenoblockers, dihydroergotamine, pizotifen) on the effectiveness or undesirable effects of Zomit.
When used together with paracetamol, metoclopramide and ergotamine, the pharmacokinetic parameters and tolerance of the drug Zomit have not been changed.
In the course of studies with the participation of healthy volunteers, it was shown that there is no clinically significant interaction between the drug Zomit and ergotamine, but theoretically, an increased risk of developing coronary vasospasm is possible. In this regard, it is recommended to observe an interval (at least 24 hours) between stopping the use of drugs containing ergotamine and prescribing Zomit. Ergotamine-containing preparations should not be prescribed earlier than 6 hours after stopping the use of Zomit.
It is necessary to exclude the use of other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors within 12 hours after taking Zomit.
A slight increase (26%) in the AUC of zolmitriptan and a three-fold increase in the AUC of its active metabolite were noted after the use of moclobemide (MAO enzyme type A inhibitor). For this reason, the recommended maximum dose of Zomit drug taken within 24 hours should not exceed 5 mg for patients taking MAO type A inhibitors at the same time.
After the use of cimetidine (an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes), an increase in T½ and AUC of zolmitriptan by 44% and 48% was noted. The T½ and AUC of the active N-demethylating metabolite are doubled, therefore, for patients receiving cimetidine, the recommended maximum dose of the drug Zomit administered within 24 hours is 5 mg.
Based on the general interaction profile of zolmitriptan, the possibility of its interaction with inhibitors of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme cannot be excluded. For this reason, when used together with such drugs (antibiotics from fluvoxamine and quinolones), it is recommended to reduce the total dose of Zomit drug taken in 24 hours to 5 mg.
After administration of rifampicin, no clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of zolmitriptan and its active metabolites were noted.
When used at the same time, it is possible to have an interaction with St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) preparations; this effect may increase the risk of developing undesirable effects (as in the case of use with other agonists of serotonin 5НТ1B/1D-receptors).
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Clinical studies have not been conducted to study the use of the drug during pregnancy. The use of Zomit during pregnancy is possible only in cases where the expected therapeutic effect for the mother is higher than the probable risk for the fetus.
The teratogenic effect of zolmitriptan was not detected in experimental studies on laboratory animals.
The decision to prescribe Zomit during lactation (breastfeeding) should be taken with caution.
Experimental studies have shown that zolmitriptan penetrates into the milk of lactating animals. There is no information on the absorption of zolmitriptan into human breast milk.
Effects on the ability to drive vehicles and other potentially dangerous mechanisms
No significant deterioration in performance of psychomotor tests was observed when Zomit was taken in a dose of up to 20 mg. It is unlikely that the use of the drug will lead to a violation of the patient’s ability to engage in potentially dangerous activities, but it is necessary to warn the patient about the development of a tendency to sleep.
Method of use and dosage
Zomit spray is not intended to prevent migraine attacks. It is recommended to use the medicine as soon as possible after a migraine attack. The recommended starting dose is 2.5 mg, which corresponds to one spray of Zomit spray at 2.5 mg/dose. The maximum recommended dose is 5 mg, which corresponds to one spray of Zomit spray at 5 mg/dose or two sprays at 2.5 mg/dose. If there is no effect of the drug or if the pain recurs, a second dose is possible no earlier than 2 hours after the first dose. The maximum daily dose is 10 mg.
Elderly patients
The safety and efficacy of Zomit spray in patients over 65 years of age have not been systematically studied.
Liver dysfunction
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of zolmitriptan nasal spray has not been studied. In patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, the breakdown of zolmitriptan after oral administration is reduced. For patients with moderate and severe liver dysfunction, it is recommended to use the drug in a maximum dose of 5 mg per day.
Kidney dysfunction
There is no need to select a dose in patients with creatinine clearance greater than 15 ml/min.
For interactions requiring dose adjustment, see the section “Interactions with other medicinal products and other types of interactions”.
Instructions for use
For Zomit spray to be more effective, you need to clean the nostrils before using it.
Before using the medicine for the first time, press the spray nozzle several times, directing the spray into the air, until a uniform spray cloud is formed. Now the medicine is ready for use.
If more than four weeks have passed since the last use of the drug, the first spray should be carried out in the air to avoid the use of an incomplete dose. The cap of the bottle containing the medicine should be kept tightly closed between uses.
When using, the bottle sprayer should be held facing upwards.
Tilt your head slightly forward, insert the spray into the nostril, tilting the tip of the spray slightly from the center of the nose and press once. If necessary, repeat the same with the other nostril.
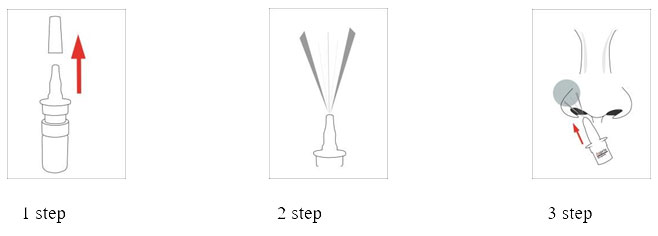
Children
The effectiveness and safety of the drug in children have not been established, so its use in this age group is not recommended.
Side effects
As a rule, the drug Zomit is well accepted by patients. Adverse reactions are mild or moderate, transient and resolve spontaneously without treatment.
Probable adverse reactions appear more often within 4 hours after taking the drug and do not increase with repeated doses.
When describing additional cases, the following frequency criteria are used: often ≥1%, but <10%; rarely ≥0.01% but <0.1%; very rarely <0.01%.
Disorders of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: often – sensory disturbances, neuropsychiatric asthenia, dizziness, feeling of heaviness and stiffness in the limbs, compression in the pharynx, neck and chest (not accompanied by ischemic changes in the ECG), paresthesias , tendency to sleep, feeling of warmth; rarely – headache.
Disturbances in the digestive system: often – nausea, dry mouth; very rarely – abdominal pain, hemorrhagic diarrhea, ischemic colitis, splenic infarction, intestinal ischemia or infarction.
Disorders of the musculoskeletal system: often – myalgia, muscle weakness.
Cardiovascular system disorders: rarely – tachycardia, heart palpitations; very rarely – angina pectoris, spasm of coronary vessels, myocardial infarction, transient arterial hypertension (very rarely observed with clinically significant symptoms).
Disorders of the urinary system: very rarely – polyuria, frequent urination.
Allergic reactions: rarely – anaphylactic reactions, angioneurotic edema, urticaria.
Overdose
Symptoms
Overuse of zolmitriptan nasal spray has not been reported. A single dose of 50 mg zolmitriptan had a sedative effect on volunteers. The elimination period of zolmitriptan after intranasal administration is 3 hours. In case of overdose, patients should be monitored for at least 15 hours or until symptoms or signs resolve.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote for zolmitriptan. In cases of severe intoxication, intensive care procedures are recommended, including ensuring the patency of the airways, adequate oxygenation and ventilation, monitoring and support of cardiovascular functions.
Packing form
2 ml (20 doses) solution in a light-proof glass vial. 1 vial is packed in a cardboard box with a leaflet.
Store condition
It should be stored at a temperature below 30°C, in a dry, dark place and out of the reach of children. Do not freeze.
Shelf life
2 years.
Do not use after the expiration date.
By prescription
Manufacturer
Farmak JSC, Ukraine. 04080, Kiev, Kirilovskaya street, 74.
